How to Choose the Right Plastic Piping for Your Plumbing Project
When it comes to plumbing projects, the choice of materials can greatly influence the durability and efficiency of your system. Plastic piping has gained popularity in recent years for its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making it a favorable option for many homeowners and contractors alike. However, with various types of plastic piping available on the market, selecting the right one can be a daunting task. Industry expert Dr. James Anderson, a renowned authority on plumbing materials, emphasizes the importance of this decision: “Understanding the specific needs of your project is key to choosing the right plastic piping that will stand the test of time.”
In this guide, we will explore the essential factors to consider when selecting plastic piping for your plumbing projects. From understanding the differences between PVC, CPVC, and PEX to evaluating the unique requirements of your water system, the information provided will equip you with the knowledge necessary for making an informed decision. By delving into the characteristics and applications of various plastic piping options, you can ensure that your plumbing installation is not only efficient but also cost-effective and long-lasting. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast, this comprehensive overview will pave the way for successful plumbing outcomes.

Understanding Different Types of Plastic Piping Materials
When selecting the right plastic piping for your plumbing projects, it is crucial to understand the different types of plastic piping materials available in the market. The most commonly used materials include Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC), and Polyethylene (PE). According to the Plastic Pipe and Fittings Association (PPFA), PVC is favored for its durability, chemical resistance, and lower installation costs, making it suitable for various applications such as drainage and venting.
CPVC, on the other hand, is recognized for its ability to withstand higher temperatures and pressure, which is essential for hot water supply lines. A study by the American Society of Plumbing Engineers (ASPE) highlights that CPVC can perform efficiently in applications where water temperatures exceed 180°F, providing a viable option for residential and commercial plumbing systems that require reliable thermal performance. Meanwhile, Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) offers excellent flexibility and resistance to impact, which makes it ideal for underground piping installations.
Selecting the appropriate plastic material also involves considering the specific requirements of your plumbing system and local building codes. Reports suggest that the growth of the global plastic piping market, projected to reach $93 billion by 2026, will be driven by the rising demand for safe and sustainable plumbing solutions across industries. Understanding these options and their respective advantages can help in making informed decisions, ensuring the efficiency and longevity of plumbing systems.
Evaluating the Strength and Durability of Plastic Pipes
When selecting plastic piping for plumbing projects, it is crucial to evaluate the strength and durability of the materials to ensure long-lasting performance. Various types of plastic pipes, such as PVC, CPVC, HDPE, and PEX, each exhibit distinct characteristics that impact their application and lifespan. According to a 2022 report by the Plastics Pipe Institute, PVC pipes can withstand pressures of up to 280 psi, making them ideal for high-pressure water applications. In terms of durability, studies indicate that PVC can have a service life exceeding 100 years when properly installed and maintained, significantly reducing the need for repairs and replacements.
Additionally, chemical resistance is a vital factor in determining the suitability of plastic pipes for different environments. CPVC pipes are particularly praised for their ability to handle higher temperatures and resist corrosion from a variety of chemicals, with a maximum operating temperature of around 200°F. A study published in the Journal of Plastic Pipe Systems highlights that PEX pipes, known for their flexibility and resistance to scale and chlorine, can last over 40 years in typical residential applications. These attributes make PEX a strong contender for both hot and cold water lines, providing homeowners and contractors with reliable options that enhance system longevity. Ultimately, choosing the right plastic piping involves balancing these factors with project-specific requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Evaluating Strength and Durability of Plastic Pipes
This chart showcases the tensile strength and impact resistance of various types of plastic piping materials commonly used in plumbing projects.
Assessing Temperature and Pressure Ratings for Plumbing Needs
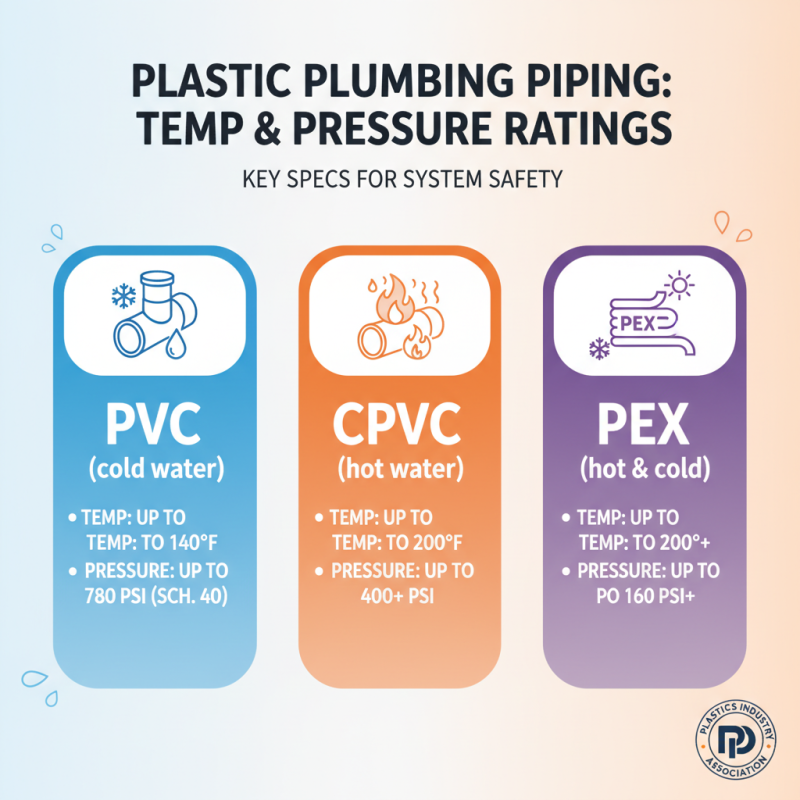
When selecting plastic piping for plumbing projects, understanding temperature and pressure ratings is crucial for ensuring system safety and efficiency. Different types of plastic piping, such as PVC, CPVC, and PEX, have distinct specifications that dictate their performance under varying conditions. According to a recent report by the Plastics Industry Association, PVC pipes can typically handle temperatures up to 140°F at a maximum working pressure of Schedule 40 (up to 780 psi). Conversely, CPVC, which is designed for hot water distribution, boasts a higher temperature threshold, operating efficiently at temperatures of 200°F and pressures exceeding 400 psi.
Moreover, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides guidelines that help in the selection process. For example, ASTM D1785 outlines the requirements for PVC piping, including their pressure ratings at various temperatures. Understanding these standards enables plumbing professionals to make informed choices when selecting plumbing materials suited to specific applications. It is essential to keep in mind that exceeding these ratings may lead to system failures, leaks, or other plumbing issues, thereby highlighting the need for careful assessment based on project requirements.
Considering Chemical Resistance in Plastic Piping Selection
When selecting plastic piping for plumbing projects, one of the most critical factors to consider is the material's chemical resistance. Different types of plastics, such as PVC, CPVC, and PEX, exhibit varying levels of durability when exposed to different chemicals and temperatures. According to industry reports from the Plastic Pipes Conference Association, PVC piping has a chemical resistance rating of about 60%, making it suitable for a variety of applications, but it may not be ideal for environments where it will come into contact with certain solvents or acids. On the other hand, CPVC offers enhanced resistance to higher temperatures and a broader range of chemicals, boasting a user-friendly profile for both hot and cold water applications.
Moreover, the chemical environment in which the piping will function is vital in ensuring long-term performance and reliability. In aggressive chemical settings, materials like PEX may be preferable due to their resistance to oxidation and a broader tolerance to various chemicals without degradation. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), the rated lifespan of PEX can exceed 50 years under proper conditions, highlighting its robustness in diverse environments. Therefore, evaluating the specific chemical interactions expected during usage can guide professionals in choosing the right plastic piping that not only meets performance requirements but also ensures safety and durability in plumbing systems.
How to Choose the Right Plastic Piping for Your Plumbing Project - Considering Chemical Resistance in Plastic Piping Selection
| Piping Material | Chemical Resistance | Temperature Range (°F) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Good for acids, salts, and chlorinated solvents | 32 to 140 | DRAINAGE, irrigation |
| CPVC | Good for hot water and various chemicals | 40 to 200 | HOT WATER, chemical processing |
| HDPE | Excellent for a wide range of chemicals | -40 to 120 | CONDUIT, water supply |
| PP | Good for alkalis and organic solvents | 32 to 190 | WASTE SYSTEMS, automotive applications |
| ABS | Limited chemical resistance | 0 to 180 | DRAINAGE, venting |
Analyzing Cost Factors and Installation Methods for Plastic Pipes
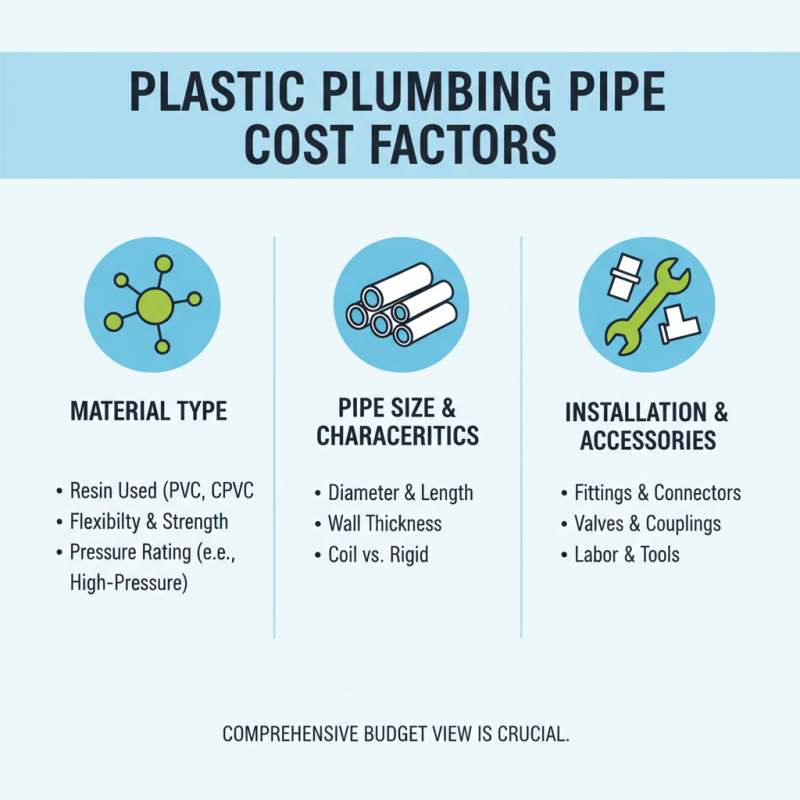
When selecting plastic piping for a plumbing project, understanding the cost factors associated with different types of materials is crucial. The price of plastic pipes can vary significantly based on the type of resin used, the size of the pipe, and the particular characteristics of the pipe, such as flexibility and strength. For instance, some pipes may be designed for high-pressure applications, which could increase their overall cost. Additionally, installation accessories and fittings may also contribute to the total expenses, making it important to take a comprehensive view of the budget when planning the project.
In terms of installation methods, the ease of working with plastic piping is one of its notable benefits. Most plastic pipes can be cut and joined with relative simplicity, often requiring less specialized labor compared to metal piping systems. Common installation techniques include solvent welding and mechanical joining, each with its own set of requirements and best practices. Proper training and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are necessary to ensure longevity and reliability in the plumbing system. Moreover, understanding local building codes can influence installation choices, as specific regulations may dictate the materials and methods deemed acceptable for different applications.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Selecting Rigid PVC Pipe: Maximize Durability and Performance Based on Industry Standards
-

Top 10 Benefits of the Plastic Moulding Process You Need to Know
-

Understanding the Applications and Advantages of PVC Extruded Profiles in Modern Construction
-

Why Understanding the Plastic Moulding Process is Essential for Manufacturers
-

Understanding the Role of Plastic Injection Moulding in Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
-

Understanding the Impact of Injection Molding Pellets on Sustainable Manufacturing Practices


